Load balancing is a networking methodology to distribute workload across multiple computers . Objective of load balancing is to achieve optimal resource utilization, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and avoid overload
Diagrammatic illustration of Load Balancing
- Load balancer’s can be Hardware or software based
- Load balancer’s support multiple algorithms like Round robin ,weighted ,Least Connection etc
- Load balancer’s support multiple protocols like HTTP , HTTPS , TCP , RTMP etc
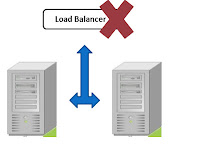
What are the problems in this Traditional Load Balancing ?
Problem 1: Load Balancer Throughput
- Sites with unpredictable load volatility patterns challenge the Load balancer throughput
- More HTTP request load on a fixed number of Load Balancers can reduce its throughput
- Very less HTTP requests load on a fixed number of load balancers will under utilize them
Load Balancer can be a Single Point Of Failure in the Architecture . To avoid that multiple Load balancer’s needs to be deployed for High Availability in the Load Balancing tier, but still the question of " How many load balancers for ensuring 100% HA ?" will be unanswered.
Problem 3: Cost effectiveness
Problem 3: Cost effectiveness
Load Balancers require additional maintenance , expertise and management effort from the IT ops. This means additional cost. Also over provisioning of Load Balancers in terms of capacity or numbers will cause unnecessary cost leakage.
What is the solution for this problem ?
Implement Amazon Elastic Load Balancing as part of your architecture.
AWS Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple Amazon EC2 instances. Elastic Load Balancing automatically scales its request handling capacity in response to incoming application traffic.
Other Load Balancing Articles :


No comments:
Post a Comment